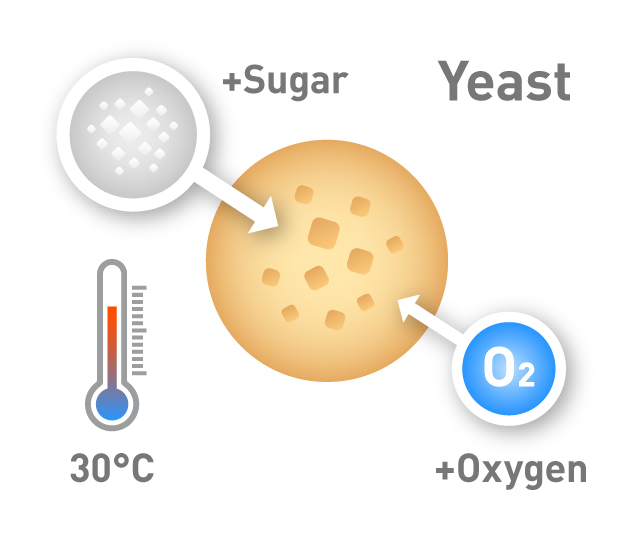
Fermented foods are rich in prebiotics and have several health benefits. However even when oxygen is abundant yeast cells prefer fermentation to aerobic respiration provided a sufficient supply of sugar is available.
Yeast Extract Production

Wild Yeast Tales Natural Merchants Organic Wine
Fermentation And Anaerobic Respiration Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy
Yeast reabsorb diacetyl that was produced during fermentation and hydrogen sulphide escapes from the top of the fermenter as a gas.

Yeast fermentation process. In ancient civilizations from Iran and Yemen to Saudi Arabia and North Africa vats of grapes were seen boiling as microscopic yeasts broke down natural sugars into molecules of alcohol of course not boiling at all but bubbling under the action of yeast consuming sugar and excreting alcohol. Fermentation Process of Penicillin. It is important to check the degree of attenuation at this point by measuring gravity to confirm that the yeast has completed fermentation.
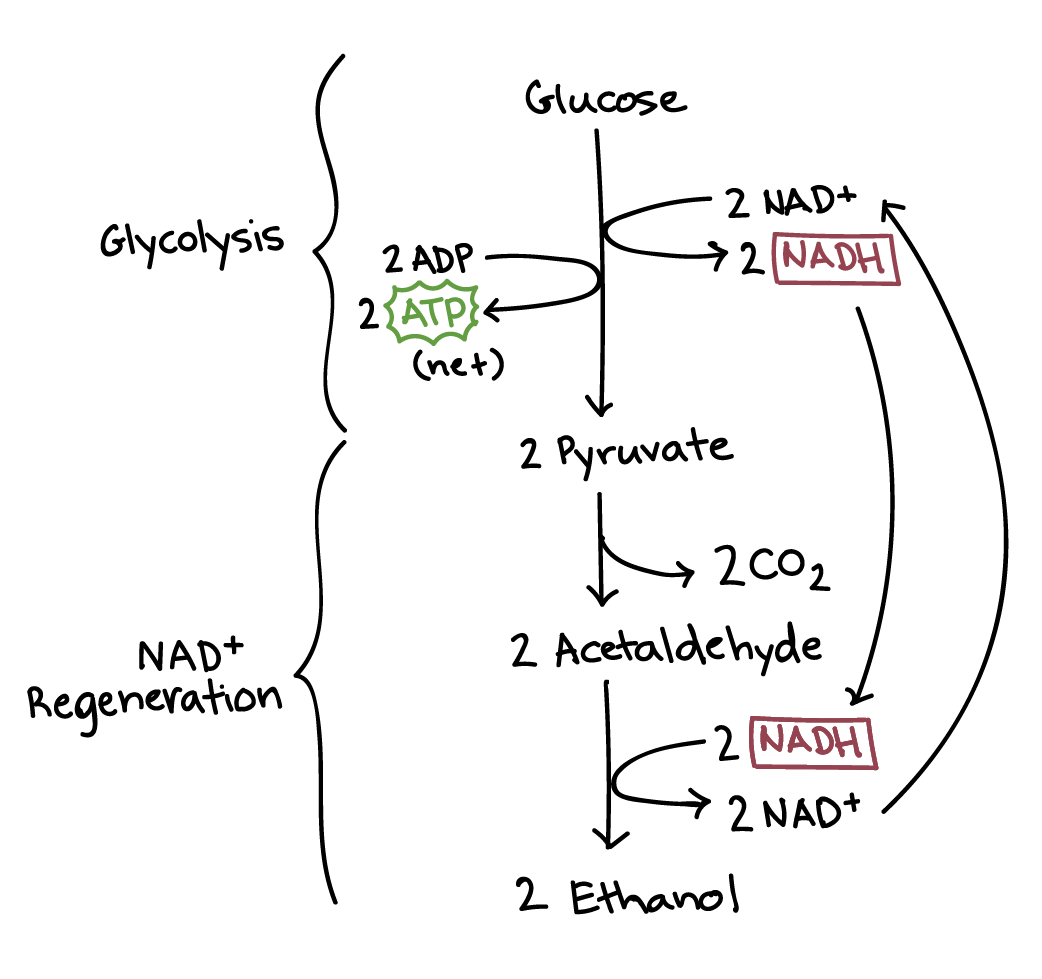
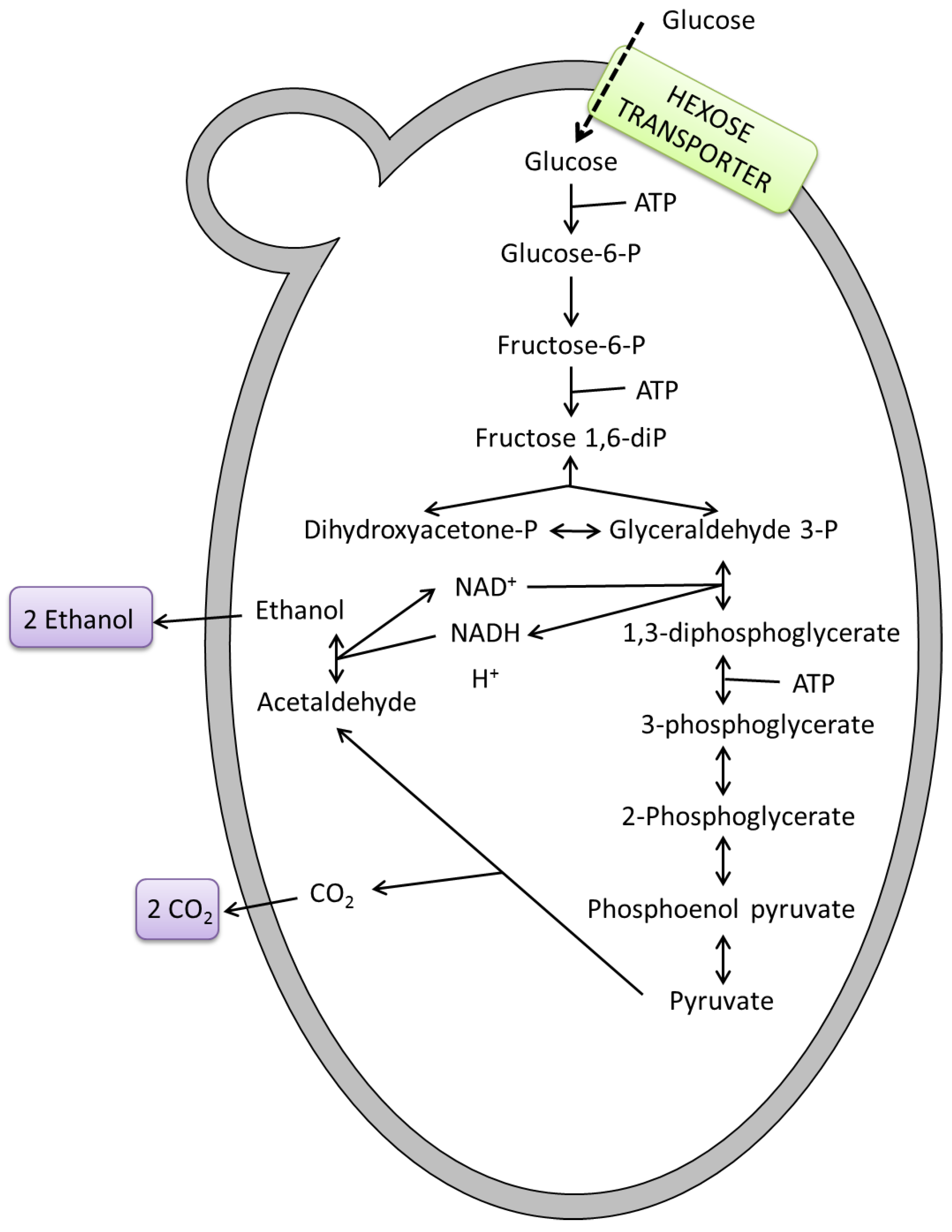
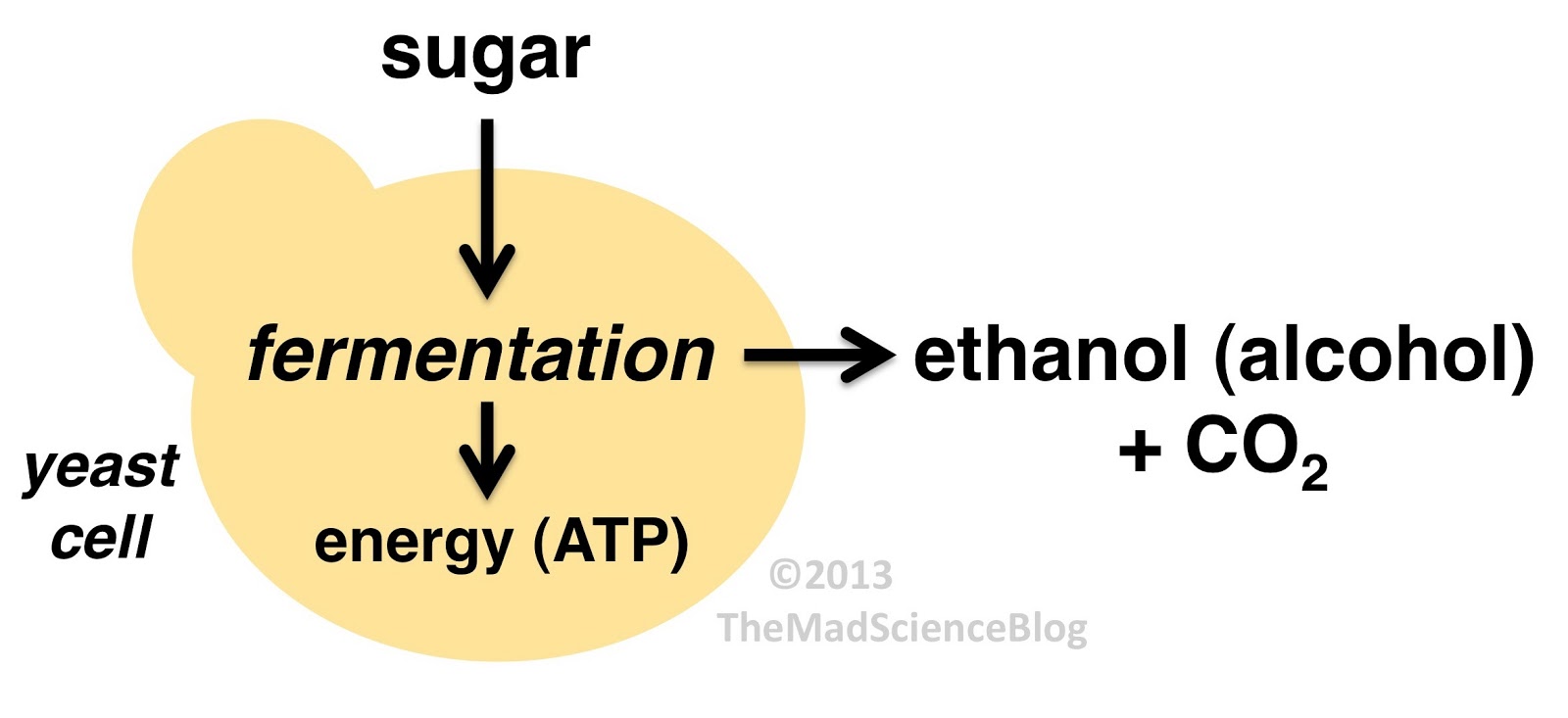
Fermentation is the process by which yeast converts the glucose in the wort to ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide gas-- giving the beer both its alcohol content and its carbonationTo begin the fermentation process the cooled wort is transferred into a fermentation vessel to. Collado-Fernández in Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition Second Edition 2003 Background. In yeast NAD is regenerated in a two-step process called alcoholic fermentation.
91342 Process Description1 Figure 9134-1 is a process flow diagram for the production of bakers yeast. This is the process that occurs in the yeast when it converts carbohydrates into energy without using oxygen. Fermentation chemical process by which molecules such as glucose are broken down anaerobically.
Some cells such as yeast even prefer fermentation to oxidative phosphorylation even if oxygen is present. Fermentation is a process whereby yeast converts glucose in the wort to ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide gas CO 2 to give beer its alcohol content and carbonationThe fermentation process starts when cooled wort is transferred to a fermenting vessel and yeast is added. Pressure fermentation is a hot topic in home brewing communities but even micro and macro breweries use pressure fermentation too.
There are different types of fermentation resulting from the action of yeast and other microorganisms such as lactic acid bacteria. Fermentation is founded on the effects of microbes in nature. The first stage of yeast production consists of growing the yeast from the pure yeast culture in a series of fermentation vessels.
Fermentation involves a complex system of reactions brought about by microorganisms that may be present simultaneously. Yeast metabolises the sugars extracted from grains which produces alcohol and carbon dioxide and thereby turns wort into beer. Fermentation on the other hand is nothing more than the opposite.
The dough fermentation process is the science behind how flour water salt and yeast come together and transform into bread. In some cases bacteria play a role too. The kraeusen falls and yeast begin to settle out or flocculate.
Fermentation is an anaerobic process meaning it does not require oxygen in order to occur. When this process is complete the wine is separated from the sediment and transferred to an aging tank. The history of yeast takes us back to 1680.
Penicillin fermentation is an aerobic process with a volumetric oxygen absorption rate of 04 -08mm min-1. Pressure fermenting isnt as straightforward as it seems though. The screening along the facade has been playfully lifted at the corners of the building giving way to full glazing to give passers-by a glimpse into the inner workings of the hub.
The required aeration rate varies according to the strain the type of fermenter used and on the impellor system. Yeast is the microorganism that is responsible for fermentation in beer. Without yeast there can be no wine.
Sirakawin Present to MsAllinotte November 21. The fermentation process is being used in the industry for making bread alcohol vinegar and other products. Fermentation is a metabolic pathway that produce ATP molecules under anaerobic conditions only undergoes glycolysis NAD is used directly in glycolysis to form ATP molecules which is not as efficient as cellular respiration because only 2ATP molecules are formed.
Yeast has an enzyme called zymase and this catalyses the fermentation process. The public areas will be designed so that visitors can get up close and personal with the fermentation process with visible fermentation vessels equipment pipes and production zones. Simply put pressure fermentation is a process that ferments beer under pressure that higher than 0 PSI Usually this is done by fermenting beer inside a closed vessel which is then pressurized.
More broadly fermentation is the foaming that occurs during the production of wine and beer a process at least 10000 years old. The dominant types of yeast used to make beer are Saccharomyces cerevisiae known as ale yeast and Saccharomyces. The interesting thing about yeasts used for beer and bread making is that they can do this conversion without oxygen even though oxygen is present.
The frothing results from the evolution of carbon dioxide gas. The biochemical process of fermentation itself creates a lot of residual heat which can take the must out of the ideal temperature range for the wine. The experiment is easy to carry out does not require expensive equipment and is suitable for introductory chemistry courses.
Here are some possible. The yeast strain pregrowth conditions its activity during the dough fermentation process the fermentation conditions as well as the dough ingredients are basic to control the process. If fermentation is not rapid because of the yeast used then the whole experiment can be carried over to the second lesson.
During fermentation there are several factors that winemakers take into consideration with the most influential to ethanol production being sugar content in the must the yeast strain used and the fermentation temperature. But it was not until 1857 and the work of French scientist Pasteur that the fermentation process was understood. The yeast is recovered from the final fermentor by using centrifugal action to concentrate the yeast solids.
Fermentation is also a way for cells to regenerate NAD which is used in glycolysis when it is coverted to NADH. Yeast Fermentation Lab Report SBI4U Chaweewan. Microbes other than yeast also impart a variety of important characteristics to beer and wine production.
Using a microscope Leeuwenhoeck observed beer yeast globules for the first time. In this paper we present a simple experiment involving the yeast-catalyzed fermentation of sugars. Glucose zymase Ethanol carbon dioxide.
Yeast is what gives wine its character aromas flavors and mouthfeel. A Guide to Beer Fermentation. The fermentation by gut bacteria protects the body from the harmful effects of ammonia.
The process of malolactic fermentation carried out by lactic acid bacteria in which malic acid is converted to lactic acid towards the end of the production of some wines may effect sensory compounds and reduce the pH of the product. In addition to fermenting the beer yeast influences the character and flavour. Enzyme catalysis 1 is an important topic which is often neglected in introductory chemistry courses.
During this second fermentation the dead yeast cells as well as other particulate matter settle to the bottom. The process of fermentation is augmented by some types of yeast and bacteria. But the role of wine yeast goes well beyond alcoholic fermentation the biochemical process of converting sugar into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
Glycolysis followed by fermentation. After the initial fermentation the liquid is allowed to ferment for 20 days to about a month. This article reveals how important dough fermentation is and deep dives into the science of bread making.
The fermentation rate is also conditioned by the ingredients of the dough including the amounts of sugar and salt used in its preparation. C 6 H 12 O 6 aq 2C 2 H 5 OHaq 2CO 2 g Student questions.

Pdf The Role Of Yeasts In Fermentation Processes

Study Of Influence Of Yeast Cells Treatment On Sugarcane Ethanol Fermentation Operating Conditions And Kinetics Sciencedirect

Alcohol Fermentation Facts Process Reaction Types

Fermentation Is A Metabolic Process Consumes Sugar With Yeast Or Bacteria In The Absence Of Oxygen

In Situ Co 2 Monitoring Experiment During A Yeast Fermentation Process Download Scientific Diagram
Microorganisms Free Full Text The Role Of Yeasts In Fermentation Processes
How Do The Products Of Fermentation In Animals Differ From Yeast Socratic
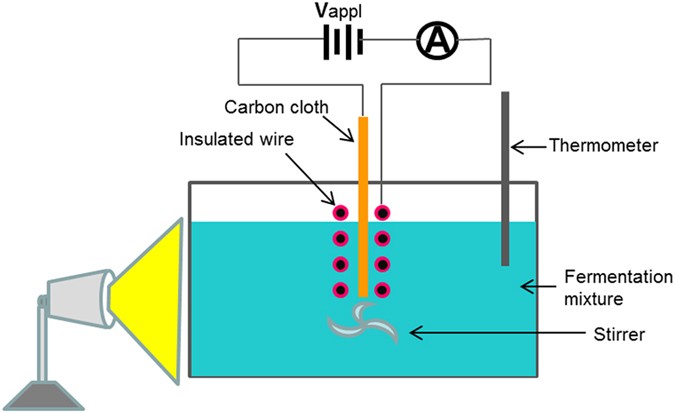
Enhanced Ethanol Production Via Electrostatically Accelerated Fermentation Of Glucose Using Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Scientific Reports

