In contrast to mitosis molecular mechanisms and regulation of meiosis are much less understood. At the end of meiosis and cytokinesis four haploid cells are produced from a single diploid cell.
File Process Of Meiosis Jpg Wikimedia Commons

The Process Of Meiosis Boundless Biology

Stages Of Meiosis Photo Credit Ali Zifan Wikimedia Commons Download Scientific Diagram
Errors during meiosis can lead to mutations in gametes.

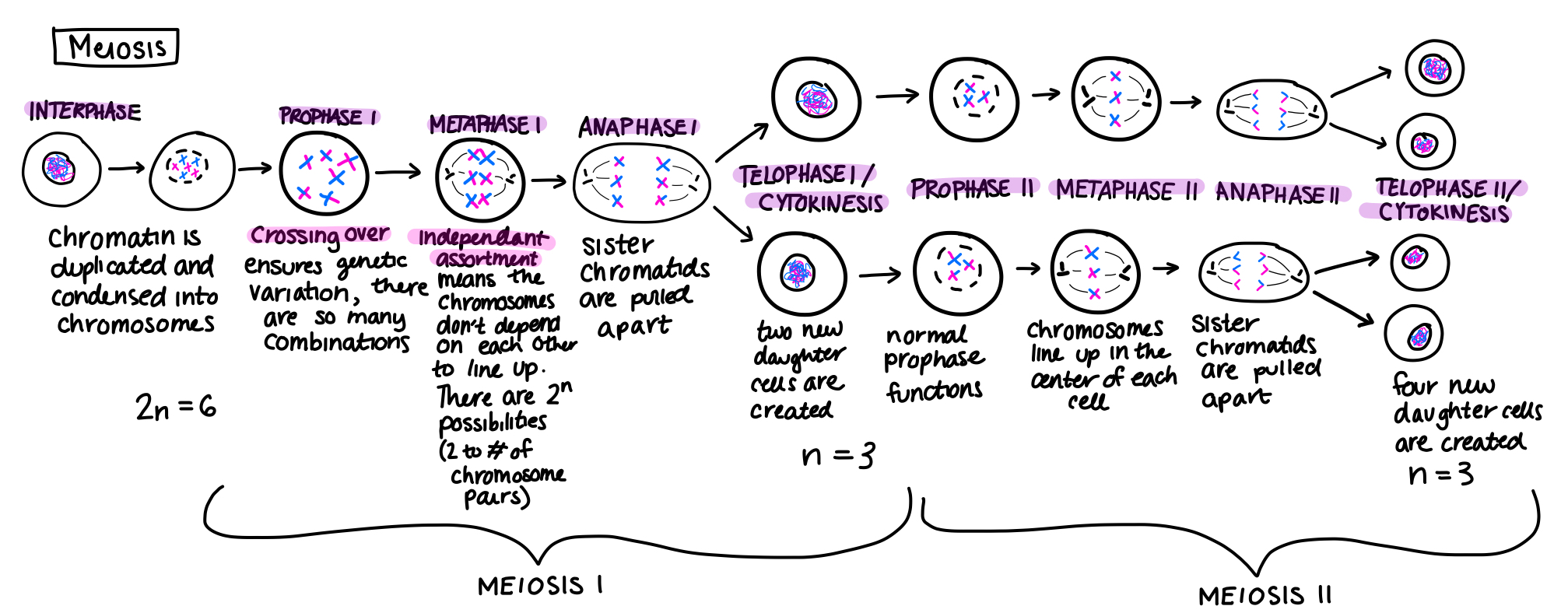
Process of meiosis. This review highlights these differences between meiosis and mitosis. An animal cell with a diploid number of four 2n 4 proceeds through the stages of meiosis to form four haploid daughter cells. Meiosis is the process by which replicated chromosomes undergo two nuclear divisions to produce four haploid cells also called meiocytes sperms and eggs.
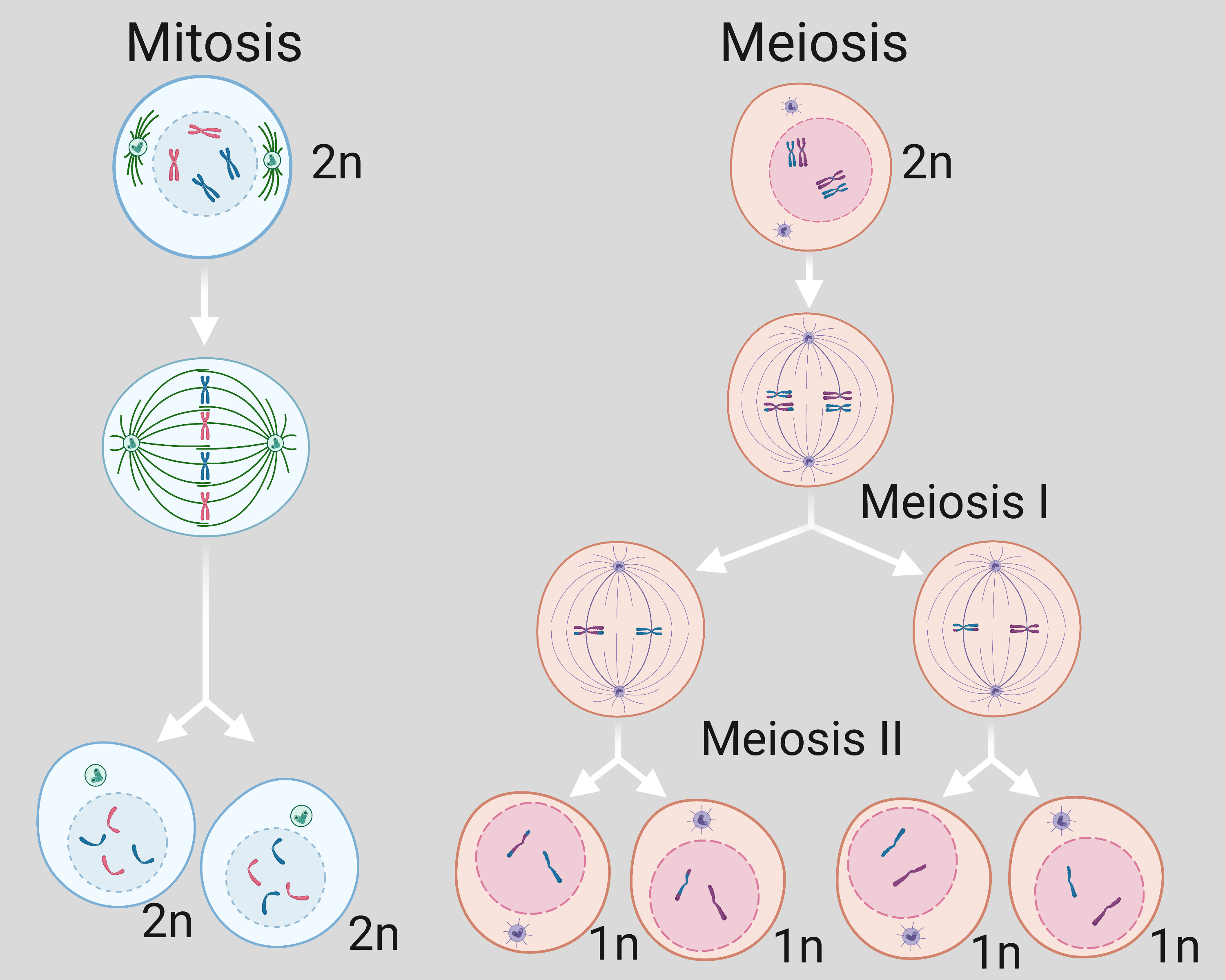
During meiosis one cell divides twice to form four daughter cells. Mitotic cell division is equational in nature while meiosis is a reduction division. Meiosis m aɪ ˈ oʊ s ɪ s.
During meiosis a small portion of each chromosome breaks off and reattaches to another chromosome. Crossing over meiosis I meiosis II and genetic variation. After meiosis the sperm and egg cells can join to create a new organism.
It reduces the chromosome number in a germ cell by half by first separating the homologous chromosomes in meiosis I and then the sister chromatids in meiosis IIThe process of meiosis I is generally longer than meiosis II because it takes. In prometaphase I microtubules attach to the fused kinetochores of homologous chromosomes and the homologous chromosomes are arranged at the midpoint of the cell in metaphase I. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half.
This process is what is behind the growth of children into adults the healing of cuts and bruises and even the regrowth of skin limbs and appendages in animals like geckos and lizards. From Ancient Greek μείωσις meiosis lessening because it is a reductional division is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms used to produce the gametes such as sperm or egg cellsIt involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome. What is Meiosis 1 Stages Process Function 2.
Meiosis shares mechanisms and regulation with mitosis in many aspects but also has critical differences from mitosis. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half. Meiosis is a two part division process that produces gametes.
Meiosis is the process by which gametes sex cells are generated in organisms that reproduce sexually. What is Meiosis 2 Stages Process Function 3. Hank gets down to the nitty gritty about meiosis the special type of cell division that is necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotic organismsCrash C.
The process of meiosis is characteristic of organisms that reproduce sexually and have a. These cells are our sex cells sperm in males eggs in females. Gametes are produced in male and female gonads and contain one-half the number of chromosomes as the original cell.
Meiosis is the process by which gametes are produced. New gene combinations are introduced in a population through the genetic recombination that occurs during meiosis. The salient features of meiotic division that make it different from mitosis are as follows-It occurs in two stages of the nuclear and cellular division as Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
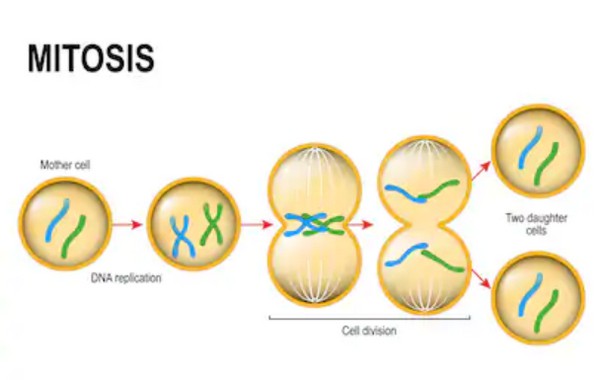
Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell divisionMitosis is the process by which most cells in the body divide involves a single round of cell division and produces two identical diploid daughter cells. These daughter cells are genetically distinct from their parent cells due to the genetic recombination which occurs in meiosis I. The chromatids of each chromosome are no longer identical because of recombination.
Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis. Defective gametes that undergo fertilization may result in miscarriages or ultimately lead to genetic disorders. In mitosis a cell makes an exact clone of itself.
Meiosis begins like mitosis. Remember homologous chromosomes have the same genes but with slight differences. Independent assortment is the process where the chromosomes move randomly to separate poles during meiosis.
The cell copies each chromosome. Mitosis is more common than meiosis and has a wider variety of functions. Meiosis I Animation 360 kb Meiosis II Animation 360 kb Meiosis II is similar to mitosis.
But unlike in mitosis homologous chromosome pairs line up and exchange pieces-a process called recombination. However there is no S phase. The process of chromosome alignment differs between meiosis I and meiosis II.
The dividing cell goes through prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase twice. Meiosis Tutorial Problem 2. If youre seeing this message it means.
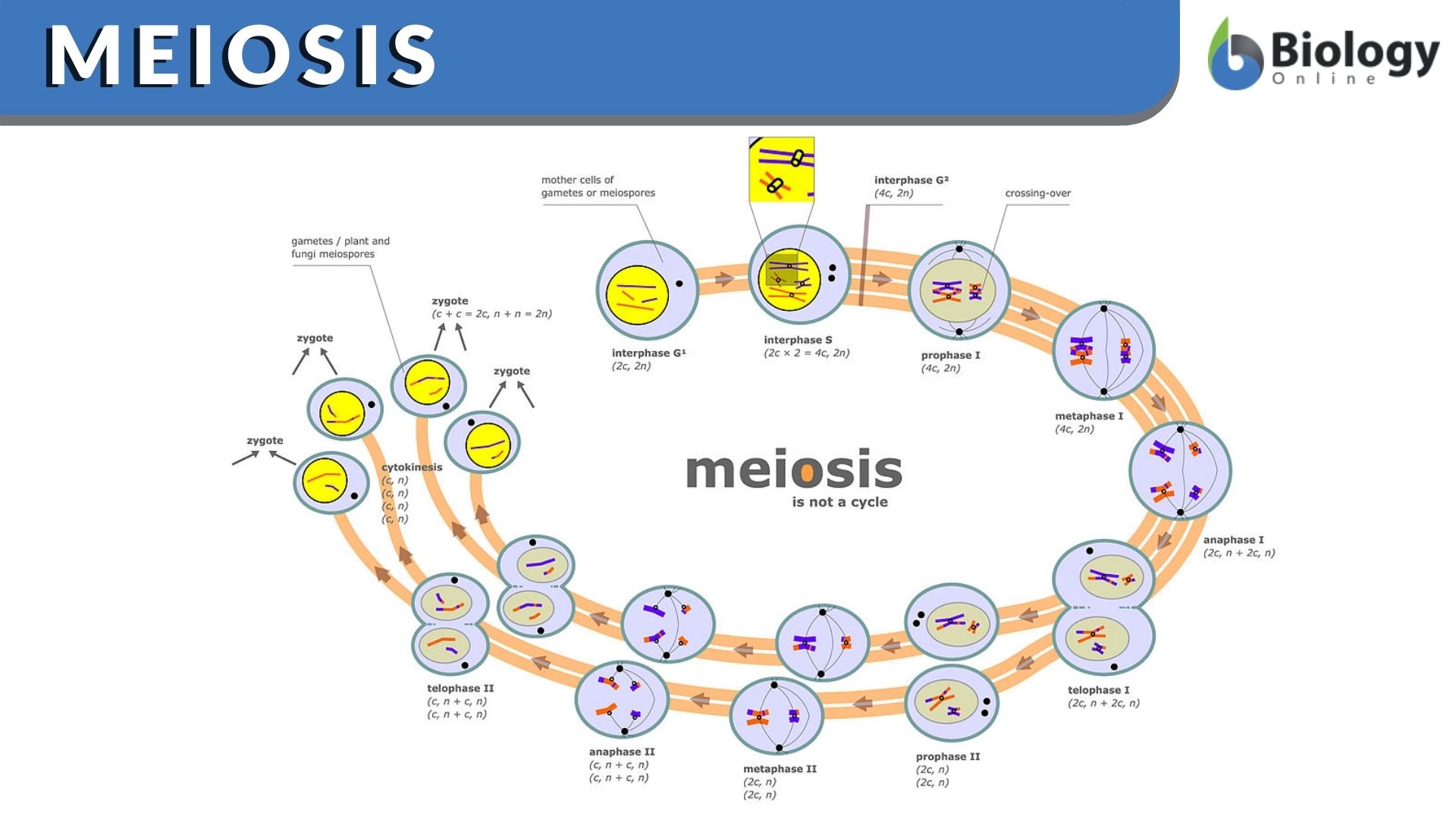
Meiosis division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes or sex cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the original cell. Many organisms package these cells into gametes such as egg and sperm. The entire process of meiosis is outlined in Figure 5.
Meiosis is a type of cell division that makes sex cells or gametes. Diploid 2 n organisms rely on meiosis to produce meiocytes which have half the ploidy of the parents for sexual reproduction. Meiosis the process by which sexually reproducing organisms generate gametes sex cells is an essential precondition for the normal formation of the embryo.
Meiosis is the process in eukaryotic sexually-reproducing animals that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction. The Biology Project Cell Biology Meiosis Problems. Meiosis has a narrow but significant purpose.
Meiosis is the specialized cell division that generates gametes. Meiosis I and Meiosis II Biology Review. Meiosis is a round of two cell divisions that results in four haploid daughter cells that each contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Meiosis is why we have genetic diversity in all sexually reproducing organisms. Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information. A gamete will end up with 23 chromosomes after meiosis but independent assortment means that each gamete will have 1 of many different combinations of chromosomes.
We now know that meiosis is the process of the production of haploid daughter cells from diploid parent cells using chromosomal reduction. DNA replication occurs however only once. Meiosis II separates the chromatids producing two daughter cells each with 23 chromosomes haploid and each chromosome has only one.
The main difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 is that during meiosis 1 chromosomal cross-over occurs at the prophase 1 leading to the genetic recombination whereas no chromosomal cross-over is identified during meiosis 2. Four different cells The process of meiosis produces four cells with nonidentical. As sexually-reproducing diploid multicellular eukaryotes humans rely on meiosis to serve a number of important functions including the promotion of genetic diversity and the creation of proper conditions for reproductive success.
Crossing over meiosis I meiosis II and genetic variation.

Meiosis Definition Stages Function And Purpose Biology Dictionary
Meiosis Cell Division
Difference Between Mitosis And Meiosis Laboratoryinfo Com
Meiosis Function Phases And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Which Phase Of Meiosis Is Different From Mitosis How Quora

The Process Of Meiosis Biology I

Meiosis Labster Theory
Rewiring Cell Division To Make Eggs And Sperm Penn Today

